This Article has been revised, edited and added to, by Poulomi Chakraborty.
- Technical SEO vs. Content SEO: A Comparative Insight
- Mobile Optimization: Catering to On-the-Go Consumers
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and HTTPS: Building Trust and Security
- Structured Data and Schema Markup: Enhancing Search Visibility
- XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt: Guiding Search Engine Crawlers
- URL Structure and Optimization: Creating Clean and Effective URLs
- Conclusion: Mastering Technical SEO for B2C Success
In the realm of digital marketing, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a cornerstone strategy that helps businesses improve their online visibility. While many focus on content and keyword strategies, technical SEO is equally critical, particularly for Business-to-Consumer (B2C) companies. Technical SEO involves optimizing the backend aspects of a website to ensure search engines can easily crawl, index, and rank it. This article delves into the essentials of technical SEO for B2C businesses, offering detailed insights and actionable tips to help you master this crucial area.
Technical SEO vs. Content SEO: A Comparative Insight

To fully appreciate the importance of technical SEO, it’s useful to compare it with content SEO. Both play vital roles in a comprehensive SEO strategy, but they focus on different aspects of optimization.
Scope and Focus
Content SEO centers around creating valuable, relevant, and engaging content that meets the needs of your audience. It involves keyword research, content creation, and on-page optimization techniques such as using appropriate headers, meta descriptions, and internal linking.
The primary goal of content SEO is to attract and engage visitors by providing them with high-quality information that answers their queries.
Technical SEO, on the other hand, deals with the structural elements of your website. It ensures that search engines can efficiently crawl and index your site, which is a prerequisite for achieving good rankings.
Technical SEO includes optimizing site speed, ensuring mobile-friendliness, securing your site with HTTPS, and implementing structured data, among other tasks. The focus here is on creating a solid foundation that supports your content SEO efforts and enhances the overall user experience.
Immediate vs. Long-Term Benefits
Content SEO often delivers more immediate results. Publishing a well-optimized blog post can quickly attract traffic and improve your rankings. High-quality content can also earn backlinks, which further boosts your SEO performance.
Technical SEO, while not as immediately visible, is essential for long-term success. Fixing site speed issues or implementing HTTPS can significantly enhance your site’s performance and security, leading to sustained improvements in rankings and user satisfaction.
Neglecting technical SEO can undermine your content efforts, as a poorly optimized site may struggle to rank, regardless of the quality of its content.
User Experience
User experience (UX) is a critical factor in both content and technical SEO. Content SEO aims to engage users with valuable information, clear formatting, and compelling visuals.
A positive user experience keeps visitors on your site longer and encourages them to explore further, which can improve your SEO metrics such as bounce rate and average session duration.
Technical SEO enhances UX by ensuring that your site loads quickly, is easy to navigate, and functions well on all devices. Elements like site speed, mobile optimization, and secure connections contribute to a seamless user experience, making visitors more likely to stay and interact with your content.
In this way, technical SEO supports and amplifies the impact of your content SEO efforts.
Site Speed and Performance
One of the most critical aspects of technical SEO is site speed. A fast-loading website provides a better user experience, reduces bounce rates, and improves search engine rankings. Users expect pages to load quickly, and even a slight delay can lead to higher bounce rates and lost opportunities for engagement and conversions.
Importance of Site Speed
Google has confirmed that site speed is a ranking factor, meaning faster sites are more likely to rank higher in search results. Additionally, a slow site can frustrate users, leading to negative user experiences and potentially damaging your brand reputation. For B2C businesses, where competition is fierce, and user expectations are high, optimizing site speed is crucial.
Techniques to Improve Site Speed
Several techniques can help improve your site’s speed and performance. First, optimize images by compressing them and using the appropriate file formats (JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics with transparent backgrounds). Tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim can help with compression without sacrificing quality.
Minimize the use of heavy scripts and plugins that can slow down your site. Combine and minify CSS and JavaScript files to reduce their size and the number of HTTP requests. Tools like UglifyJS and CSSNano can assist with this process. Implementing browser caching and using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can also enhance performance by reducing load times and improving site responsiveness.
Mobile Optimization: Catering to On-the-Go Consumers

With the rise of mobile internet usage, optimizing your website for mobile devices is no longer optional; it’s essential. Mobile optimization ensures that your website provides a seamless experience across all devices, which is crucial for retaining visitors and improving search engine rankings.
The Importance of Mobile Optimization
Google’s mobile-first indexing means that the mobile version of your website is considered the primary version for indexing and ranking. This shift underscores the importance of mobile optimization for B2C businesses.
Consumers increasingly use mobile devices to browse, shop, and interact with brands, making it vital to ensure your site performs well on smartphones and tablets.
Enhancing User Experience
A mobile-optimized website provides a better user experience, which can lead to higher engagement, longer session durations, and lower bounce rates. When users can easily navigate your site, read content, and complete transactions on their mobile devices, they are more likely to stay and convert.
Boosting SEO Performance
Mobile optimization is a significant ranking factor for search engines. Sites that offer a poor mobile experience may see a drop in rankings, while those that are mobile-friendly can benefit from improved visibility. This is particularly important for B2C businesses, where a large portion of traffic often comes from mobile searches.
Techniques for Mobile Optimization
Several techniques can help ensure your website is fully optimized for mobile devices. These strategies focus on improving usability, speed, and overall performance.
Responsive Design
A responsive design automatically adjusts your website’s layout to fit different screen sizes and orientations. This ensures a consistent and user-friendly experience across desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
Implementing responsive design involves using flexible grid layouts, fluid images, and CSS media queries to adapt your site to various devices.
Simplified Navigation
Mobile users often interact with websites differently than desktop users. Simplified navigation is crucial for a positive mobile experience. Use a clean, easy-to-use menu system that allows users to find what they need quickly.
Hamburger menus, which expand to show navigation options, are a popular choice for mobile sites as they save space and reduce clutter.
Fast Load Times
Speed is even more critical on mobile devices, where users may have slower internet connections. Optimize images and reduce the number of heavy scripts and plugins to ensure fast load times.
Implement Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) to create stripped-down versions of your pages that load quickly on mobile devices. AMP can significantly improve load times, enhance user experience, and boost search engine rankings.
Touch-Friendly Design
Ensure that all interactive elements, such as buttons and links, are touch-friendly. This means making them large enough to be easily tapped and spaced adequately to prevent accidental clicks. Touch-friendly design enhances usability and reduces frustration for mobile users.
Testing and Monitoring Mobile Performance
Regularly testing and monitoring your website’s mobile performance is essential to ensure it continues to meet user expectations and SEO standards.
Mobile Usability Testing
Use tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check how well your site performs on mobile devices. This tool provides insights into potential issues and areas for improvement. Additionally, manually testing your site on various devices and screen sizes can help you identify usability problems and ensure a consistent experience.
Monitoring Mobile Metrics
Google Analytics offers valuable data on mobile performance. Monitor metrics such as bounce rate, average session duration, and conversion rates for mobile users. Analyzing this data helps you understand how mobile visitors interact with your site and where improvements are needed.
Adapting to Changing Mobile Trends
Mobile technology and user behavior are constantly evolving. Staying updated with the latest trends and best practices in mobile optimization is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Keeping Up with Mobile Innovations
Keep an eye on emerging mobile technologies and innovations that can enhance user experience. For instance, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) combine the best of web and mobile apps, offering fast load times, offline access, and a native app-like experience. Adopting such technologies can set your site apart and provide a superior mobile experience.
Regular Updates and Maintenance
Regularly updating your site to incorporate new mobile optimization techniques ensures that it remains relevant and effective. Perform periodic audits to identify and address any issues that may arise as mobile technology evolves. Continuous maintenance and improvement are key to delivering a top-notch mobile experience.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and HTTPS: Building Trust and Security

In today’s digital landscape, security is paramount, especially for B2C businesses that handle sensitive customer information. Implementing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and ensuring your website uses HTTPS is essential for protecting data, building trust with your audience, and improving your search engine rankings.
The Importance of SSL and HTTPS
SSL is a security protocol that encrypts data transmitted between a user’s browser and your web server. HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is the secure version of HTTP, enabled by SSL.
Together, they provide a secure connection that protects sensitive information, such as personal details and payment data, from being intercepted by malicious actors.
Enhancing User Trust
When users see the padlock icon and “https://” in the address bar, they know that their connection to your site is secure. This visual cue enhances trust and confidence, making visitors more likely to complete transactions and share personal information. For B2C businesses, building trust is crucial for converting visitors into customers.
Boosting SEO Performance
Google has confirmed that HTTPS is a ranking signal, meaning secure sites are more likely to rank higher in search results. Implementing SSL can give your site a competitive edge, potentially leading to increased visibility and traffic. Additionally, some browsers display warnings for non-HTTPS sites, which can deter users and negatively impact your reputation.
Implementing SSL and HTTPS
Implementing SSL and ensuring your site uses HTTPS involves several steps, from purchasing an SSL certificate to configuring your server and updating your site’s URLs.
Purchasing an SSL Certificate
First, you need to purchase an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA). Many hosting providers offer SSL certificates as part of their packages, or you can use free options like Let’s Encrypt. Choose a certificate that meets your needs, whether it’s a single-domain, multi-domain, or wildcard certificate.
Installing the SSL Certificate
After purchasing the SSL certificate, you’ll need to install it on your web server. The installation process varies depending on your hosting provider and server configuration, but most providers offer detailed instructions or support to help you through the process.
Updating Your Website URLs
Once the SSL certificate is installed, update your website’s URLs to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. This involves changing the URLs in your content management system (CMS), internal links, and any references to your site in external resources.
It’s also essential to set up 301 redirects from the HTTP versions of your pages to the HTTPS versions to ensure that visitors are automatically directed to the secure site.
Verifying and Testing
After implementing SSL and updating your URLs, verify that your site is correctly configured. Use tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test to check the security of your SSL certificate and identify any potential issues.
Additionally, manually test your site to ensure that all pages load correctly and that there are no mixed content warnings (when a page is loaded over HTTPS but contains elements, such as images or scripts, loaded over HTTP).
Maintaining SSL and HTTPS
Maintaining your SSL and HTTPS implementation is crucial for ongoing security and performance. Regularly renew your SSL certificate, monitor your site for any security issues, and stay updated with best practices in web security.
Regular Renewal
SSL certificates have expiration dates and must be renewed periodically (typically every year or two). Set reminders to renew your certificate before it expires to avoid any disruptions to your site’s security.
Monitoring and Updates
Regularly monitor your site for any security vulnerabilities and update your SSL configuration as needed. Stay informed about the latest developments in web security to ensure that your site remains protected against emerging threats.
Benefits Beyond Security
Implementing SSL and HTTPS offers benefits beyond security and SEO. It enhances your site’s overall user experience by providing faster load times and improved performance.
Faster Load Times
HTTPS can improve your site’s performance due to the use of HTTP/2, a major revision of the HTTP network protocol. HTTP/2 includes features like multiplexing, header compression, and server push, which can significantly reduce page load times and enhance the user experience.
Improved Analytics Data
Using HTTPS can also improve the accuracy of your analytics data. When traffic passes from an HTTPS site to an HTTP site, the referral data can be lost, and the traffic may be misattributed as “direct” traffic. By using HTTPS, you ensure that referral data is preserved, providing a more accurate picture of your traffic sources.

Structured Data and Schema Markup: Enhancing Search Visibility
Structured data and schema markup are powerful tools in the realm of technical SEO. They help search engines understand the content on your website more effectively, which can enhance your visibility in search results through rich snippets and other advanced features.
What is Structured Data?
Structured data refers to a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content. It helps search engines interpret the data on your site, allowing them to display it in a more meaningful way in search results. Structured data is implemented using a specific vocabulary called schema markup.
The Benefits of Schema Markup
Implementing schema markup can significantly boost your SEO efforts by improving how your site’s information is displayed in search results. This not only enhances your visibility but also increases click-through rates by providing users with more detailed and relevant information directly in the search results.
Rich Snippets
Rich snippets are enhanced search results that include additional information, such as reviews, ratings, prices, and other relevant details. These snippets make your listing more attractive and informative, which can lead to higher click-through rates. For example, a rich snippet for a product page might show the product’s average rating, price, and availability.
Knowledge Graph and Rich Cards
The Knowledge Graph is a feature that displays information about entities (people, places, organizations) in a panel on the right side of the search results. Implementing schema markup can help your content appear in the Knowledge Graph, providing users with quick access to relevant information about your brand.
Rich cards are a mobile-friendly version of rich snippets that use a card-like format to present content. They are designed to improve the user experience on mobile devices and can enhance your site’s visibility in mobile search results.
Types of Schema Markup for B2C Websites
Several types of schema markup can be particularly beneficial for B2C websites. These include product markup, review markup, and local business markup.
Product Markup
Product markup provides detailed information about your products, such as name, description, price, availability, and reviews. Implementing product markup helps search engines display this information in rich snippets, making your products stand out in search results. This can drive more traffic to your site and increase conversions.
Review Markup
Review markup allows you to display customer reviews and ratings in search results. Reviews play a significant role in consumer decision-making, and showcasing positive feedback can build trust and credibility. Review markup can also improve your site’s visibility and click-through rates by highlighting user-generated content.
Local Business Markup
Local business markup is essential for businesses with a physical location. It provides information such as your business name, address, phone number, hours of operation, and geographic coordinates. This data helps search engines display your business in local search results and maps, making it easier for customers to find you.
Implementing Schema Markup
Implementing schema markup involves adding specific code to your website’s HTML. While this may sound technical, there are tools and resources available to simplify the process.
Using Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper is a user-friendly tool that guides you through the process of adding schema markup to your site. You simply highlight the relevant information on your page, and the tool generates the appropriate markup code. You can then add this code to your HTML.
Testing Your Markup
Once you have implemented schema markup, it’s important to test it to ensure it’s working correctly. Google’s Rich Results Test allows you to enter a URL or code snippet to check if the structured data is valid and preview how it will appear in search results. This helps identify any errors or issues that need to be fixed.
Best Practices for Structured Data
To get the most out of structured data and schema markup, follow these best practices:
Accuracy and Relevance
Ensure that the information you mark up is accurate and relevant. Providing misleading or incorrect information can harm your credibility and negatively impact your SEO efforts. Keep your structured data up to date, especially for dynamic elements like product availability and prices.
Avoiding Overuse
While schema markup can enhance your search visibility, it’s important not to overuse it. Focus on marking up the most critical elements of your content. Overloading your pages with unnecessary markup can lead to confusion and may not provide additional SEO benefits.
Following Guidelines
Adhere to the guidelines provided by search engines like Google. Each type of structured data has specific requirements and recommendations. Following these guidelines ensures that your markup is correctly interpreted and displayed by search engines.
The Future of Structured Data
As search engines continue to evolve, the role of structured data is likely to grow. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning mean that search engines are becoming better at understanding and utilizing structured data.
Staying updated with the latest developments and best practices in schema markup will help you maintain a competitive edge and maximize your search visibility.
XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt: Guiding Search Engine Crawlers

Ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl and index your website is a fundamental aspect of technical SEO. XML sitemaps and the robots.txt file are essential tools for guiding search engine crawlers and optimizing the discoverability of your site’s content.
Understanding XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website, helping search engines understand the structure of your site and discover new or updated content. XML sitemaps provide valuable information about each page, such as its priority, last modification date, and frequency of updates.
The Role of XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps are particularly useful for large websites with complex structures, new websites with few external links, and websites with rich media content or dynamically generated pages. By providing a roadmap of your site, XML sitemaps ensure that search engines can efficiently crawl and index all your important pages.
Creating an XML Sitemap
Creating an XML sitemap can be done manually or using various tools and plugins. For instance, if you use a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO or Google XML Sitemaps can automatically generate and update your sitemap. These tools simplify the process and ensure that your sitemap remains current as you add or update content.
Submitting Your XML Sitemap
Once you have created your XML sitemap, you need to submit it to search engines. For Google, you can do this through the Google Search Console. Navigate to the “Sitemaps” section, enter the URL of your sitemap, and submit it. This step helps Google discover your sitemap and start crawling your site more effectively.
The Function of Robots.txt
The robots.txt file is a simple text file placed in the root directory of your website. It provides instructions to search engine crawlers about which pages or sections of your site should not be crawled or indexed. This file is useful for controlling crawler access and optimizing your crawl budget.
Why Use Robots.txt?
Using the robots.txt file can help you manage crawler behavior and protect sensitive or irrelevant content from being indexed. For example, you might want to block crawlers from accessing admin pages, internal search results, duplicate content, or staging versions of your site.
By doing so, you ensure that search engines focus on indexing the most valuable and relevant content.
Creating and Configuring Robots.txt
Creating a robots.txt file involves adding specific directives that tell search engines what to do. Here’s a basic example of a robots.txt file:
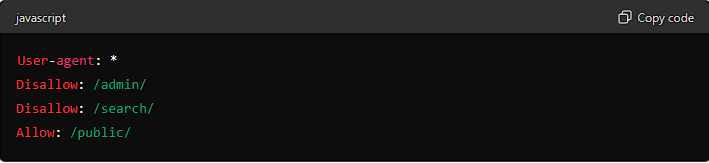
In this example, the User-agent: * directive applies the rules to all crawlers. The Disallow directives prevent crawlers from accessing the /admin/ and /search/ directories, while the Allow directive explicitly permits crawling of the /public/ directory.
Best Practices for Robots.txt
When configuring your robots.txt file, follow these best practices to ensure it effectively guides crawlers:
- Keep it Simple: Use clear and straightforward directives to avoid confusion. Overly complex rules can lead to unintended blocking of important pages.
- Test Your File: Use tools like Google’s Robots.txt Tester in the Search Console to check for errors and ensure that your directives are correctly implemented.
- Regularly Update and Monitor: As your website evolves, update your robots.txt file to reflect any changes in your content structure or crawling preferences. Regularly monitor your site’s indexing status to identify and address any issues.
Balancing Crawl Efficiency and Visibility
Both XML sitemaps and the robots.txt file play crucial roles in balancing crawl efficiency and visibility. By providing a comprehensive sitemap, you help search engines efficiently discover and index your important pages. Simultaneously, the robots.txt file allows you to manage crawler access and prioritize high-value content.
Prioritizing Important Pages
Use your XML sitemap to prioritize important pages by assigning higher priority values to those that are critical to your business, such as product pages, landing pages, and high-performing blog posts. This helps search engines understand which pages are most significant and should be crawled more frequently.
Managing Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and dilute your SEO efforts. Use the robots.txt file to prevent crawlers from indexing duplicate pages or unnecessary variations, such as session IDs or tracking parameters. Additionally, consider using canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page when duplicates are necessary.
Monitoring and Adjusting Strategies
Regular monitoring and adjustment of your XML sitemap and robots.txt file are essential for maintaining an effective SEO strategy. As your site grows and changes, ensure that these files are updated to reflect new content, structural changes, and evolving SEO priorities.
Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides valuable insights into how your site is being crawled and indexed. Regularly check the “Coverage” and “Sitemaps” sections to identify any issues, such as crawl errors, blocked pages, or missing content. Addressing these issues promptly can help maintain optimal crawl efficiency and visibility.
Adapting to Changes
SEO is a dynamic field, and search engine algorithms continually evolve. Stay informed about the latest best practices and updates from search engines to ensure that your XML sitemap and robots.txt file remain effective tools for guiding crawlers and optimizing your site’s performance.
URL Structure and Optimization: Creating Clean and Effective URLs

A well-structured URL is essential for both user experience and SEO. Clean and descriptive URLs help search engines understand the content of your pages, improve your site’s crawlability, and provide a better experience for users. This section explores the importance of URL optimization and offers practical tips for creating effective URLs.
The Importance of URL Structure
URLs are one of the first elements that search engines and users encounter when accessing a page. A well-structured URL provides clear information about the page’s content and its place within the website’s hierarchy. This can enhance both search engine rankings and user engagement.
SEO Benefits
Search engines use URLs to understand the content and context of a page. Including relevant keywords in your URLs can improve your search engine rankings for those terms. Additionally, clean and concise URLs are easier for search engines to crawl, which can improve your site’s overall crawlability and indexing.
User Experience
For users, a well-structured URL can provide immediate context about the page’s content, helping them decide whether to click on the link. Clean URLs are also easier to read and remember, enhancing the overall user experience.
Best Practices for URL Structure
Creating effective URLs involves several best practices that focus on clarity, simplicity, and relevance. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your URLs are optimized for both search engines and users.
Keeping URLs Short and Descriptive
Short URLs are easier to read, remember, and share. Aim to keep your URLs concise while including enough information to describe the page’s content. Avoid unnecessary words, parameters, or characters that can clutter the URL and make it difficult to understand.
For example, instead of using a long, complex URL like www.example.com/blog/2023/03/20/how-to-improve-your-seo-with-these-10-simple-tips.html, opt for a shorter version like www.example.com/blog/seo-tips.
Using Hyphens to Separate Words
Hyphens are the preferred method for separating words in URLs. They improve readability for both search engines and users. Avoid using underscores or other characters, as these can be harder to read and may not be interpreted correctly by search engines.
For instance, use www.example.com/seo-tips rather than www.example.com/seo_tips or www.example.com/seotips.
Incorporating Keywords
Including relevant keywords in your URLs can enhance your SEO by signaling to search engines what the page is about. However, avoid keyword stuffing or forcing keywords into the URL unnaturally. The URL should flow naturally and make sense to users.
For example, if your page is about best practices for SEO, a good URL might be www.example.com/seo-best-practices.
Avoiding Dynamic Parameters
Dynamic URLs with complex parameters can be difficult for search engines to crawl and index. Whenever possible, use static URLs that are more readable and SEO-friendly. If you must use parameters, try to limit their number and ensure they are meaningful.
Instead of using a dynamic URL like www.example.com/index.php?id=123&sort=asc&category=seo, consider a static version like www.example.com/seo/basics.
Managing URL Redirects
Redirects are an important aspect of URL management, particularly when you make changes to your site structure or content. Properly managing redirects ensures that users and search engines are directed to the correct pages, preserving your SEO efforts and providing a smooth user experience.
Using 301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that passes the majority of the original page’s link equity to the new page. Use 301 redirects when you move content to a new URL or make changes to your site’s structure. This helps preserve your SEO rankings and ensures that visitors are directed to the correct page.
For example, if you change a URL from www.example.com/old-page to www.example.com/new-page, set up a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one.
Avoiding Redirect Chains
Redirect chains occur when multiple redirects are used in sequence, such as a URL redirecting to another URL, which then redirects to yet another URL. Redirect chains can slow down page load times and dilute link equity. Aim to have a single, direct redirect whenever possible to maintain SEO value and improve user experience.
For instance, if www.example.com/page1 redirects to www.example.com/page2, and www.example.com/page2 redirects to www.example.com/page3, consolidate the redirects so that www.example.com/page1 directly redirects to www.example.com/page3.
Canonicalization
Canonicalization is the process of specifying the preferred version of a URL when multiple versions of the same content exist. Using canonical tags helps prevent duplicate content issues and ensures that search engines understand which version of the page to index.
Implementing Canonical Tags
Add a canonical tag to the head section of your HTML code to indicate the preferred URL for a page. This tag should point to the canonical version of the content, consolidating link equity and avoiding duplicate content penalties.
For example, if you have multiple URLs for the same content, such as www.example.com/page and www.example.com/page?ref=123, use a canonical tag on both versions that points to the preferred URL: <link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/page">.
Benefits of Canonicalization
Canonicalization helps search engines understand your content structure, reduces the risk of duplicate content issues, and ensures that your preferred version of a page receives the most link equity. This can improve your search engine rankings and provide a clearer, more consistent user experience.
Monitoring and Maintaining URL Health
Regularly monitoring and maintaining your URLs is essential for long-term SEO success. Use tools like Google Search Console to check for crawl errors, broken links, and other issues that may affect your site’s performance.
Fixing Broken Links
Broken links can harm your SEO and provide a poor user experience. Regularly check for and fix broken links by updating or removing outdated URLs. Tools like Screaming Frog and Ahrefs can help you identify broken links on your site.
Updating Internal Links
When you update your URLs, ensure that your internal links are also updated to reflect the new structure. Consistent and accurate internal linking helps search engines crawl your site more effectively and improves navigation for users.
Conclusion: Mastering Technical SEO for B2C Success
Technical SEO is the backbone of a successful B2C website, ensuring that your site is easily accessible, fast, secure, and user-friendly. By focusing on elements such as mobile optimization, SSL implementation, structured data, and effective URL management, you create a solid foundation that supports your content and marketing efforts.
These technical optimizations not only improve your search engine rankings but also enhance the overall user experience, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates. Staying updated with the latest SEO best practices and continuously monitoring your site’s performance will keep you ahead of the competition. Embrace these technical SEO essentials to build a robust online presence and drive sustainable growth for your B2C business.
READ NEXT:
- Money 101: SEO for Financial Literacy Programs
- Trust the Experts: SEO for Financial Advisers
- An Introduction to SEO for Financial Services
- Keyword Research Basics for Financial Services SEO
- The Ultimate Guide to Capturing Credit Card Shoppers Through SEO



















Comments are closed.