This Article has been revised, edited and added to, by Poulomi Chakraborty.
- Related: Check out our free SEO suite
- JavaScript: The Double-Edged Sword for SEO
- Enhancing SEO with JavaScript: The Strategic Playbook
- Advanced Performance Optimization: Speed Matters
- Mobile-First Development and SEO
- The Role of A/B Testing in SEO and User Experience
- Continual Learning and Adaptation
- Implementing Code Splitting in Your JavaScript Application
- Examples Of Implementing These Practices
- Conclusion
Welcome to the vibrant world of JavaScript and on-page SEO, where the melding of programming and optimization paints the future of web development. In an era where websites are more dynamic than ever, understanding how JavaScript impacts your SEO is akin to holding the key to the digital kingdom. This guide isn’t just a collection of best practices; it’s a journey into optimizing your web presence with the power of JavaScript, all while keeping it light, engaging, and actionable. Let’s dive into the intricacies of JavaScript and SEO, and uncover how you can harness these forces in harmony.
JavaScript: The Double-Edged Sword for SEO
JavaScript, the backbone of interactive websites, has transformed the web from static pages into dynamic experiences. However, its impact on SEO is a tale of two cities. On one hand, JavaScript can enrich user engagement through interactive features; on the other, it poses challenges for search engine crawlers. The crux lies in understanding this duality to leverage JavaScript for enhancing, rather than hindering, your website’s SEO.
Understanding JavaScript’s Impact on Search Engines
Search engines like Google have evolved to crawl and index JavaScript-based content more effectively than before. Yet, the process isn’t flawless. The primary challenge arises from how search engines interpret JavaScript. Unlike humans, search engines need to render JavaScript to see the content it generates, which can lead to delays or discrepancies in indexing this content.
For SEO, the timing and accuracy of content indexing are crucial. If search engine bots struggle to render JavaScript, it can delay the indexing of your site’s content, impacting its visibility and ranking. This brings us to an essential comparison: JavaScript rendering versus static HTML in terms of search engine friendliness.

In my role as a product designer and marketing consultant, particularly with Adaptify AI, I’ve harnessed JavaScript to enhance user experiences without sacrificing on-page SEO.
One technique that has proven effective is server-side rendering (SSR). This approach allows us to load the critical HTML content on the server first, making sure it’s crawlable by search engines before JavaScript enriches the user interface on the client side.
This dual rendering ensures robust SEO while maintaining dynamic interactivity essential for a modern web experience. The blending of JavaScript in web development comes with its share of challenges, primarily around load times and SEO visibility.
During my previous projects, including a redesign for a fintech startup, addressing JavaScript’s impact on SEO meant implementing asynchronous loading.
This allowed us to defer loading non-critical JavaScript, ensuring essential content was accessible to search engines at the initial load, greatly enhancing site performance and SEO metrics.
For startups eager to bring together JavaScript and SEO effectively, consider using tools like Google Lighthouse to regularly review your site’s performance.
It helps in identifying and optimizing scripts that slow down your site, providing practical suggestions for improvement. Specifically, minify and defer non-critical JavaScript and use code splitting to load scripts as needed rather than all at once.
Emphasizing these strategies in past projects not only boosted our client sites in search rankings but also significantly improved user engagement by speeding up interactive functionalities.

In my role as the founder and CEO of Cleartail Marketing, I’ve encountered various challenges and opportunities while integrating JavaScript into websites with a strong focus on maintaining robust on-page SEO.
One effective tactic we’ve utilized is progressive enhancement. This approach ensures the essential content loads first and is crawlable by search engines, while more sophisticated JavaScript functionalities are then layered on top.
This method not only secures SEO benefits but also caters to users with more advanced browser capabilities without penalizing the user experience.
A specific challenge we faced was the JavaScript-heavy features impacting site load time, which is crucial for SEO. To mitigate this without stripping away dynamic features, we implemented code splitting.
This technique involves dividing JavaScript into smaller, manageable chunks that are loaded as needed rather than in one large, initial load.
This greatly improved load times and, consequently, our SEO performance. Using tools like Google’s Lighthouse to monitor and adjust this approach helped us identify which scripts were essential and how their loading impact could be minimized.
For startups aiming to optimize their use of JavaScript for better visibility in search engines, I recommend prioritizing the user experience alongside technical SEO requirements.
Be strategic about the scripts you use, ensure they are necessary, and leverage asynchronous and deferred loading to mitigate any negative impacts on page load times.
Regular audits with tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can offer actionable insights to continuously refine your approach, ensuring that both SEO and user interaction are optimized.
Additionally, keep abreast of the latest SEO and JavaScript trends to adapt and refine your strategies, as both fields are constantly evolving.

Navigating the integration of JavaScript without compromising on-page SEO has been a core focus in my journey through the digital marketing and software space.
In my role as a founder of multiple startups, particularly in software and digital marketing, I’ve had experience in striking a balance between functionality and SEO.
One successful strategy has been utilizing Hybrid Rendering, where critical content is rendered server-side and less SEO-critical interactions are handled client-side.
This approach maintains functionality without sacrificing search engine visibility. One challenge that often surfaces with JavaScript is the potential for it to delay the indexing of crucial content.
To overcome this, we have utilized a strategy that combines the defer and async attributes for JavaScript files, ensuring that the page’s main content is loaded and indexed by search engines before any JavaScript-enhanced features.
This careful script management has significantly smoothed our SEO performance, optimizing load times and improving user engagement metrics, key factors in SEO ranking.
For startups aiming to harness the power of JavaScript without hampering their SEO efforts, I recommend focusing on critical rendering paths and making use of tools like Google’s Lighthouse and Chrome DevTools.
These tools provide invaluable insights into how JavaScript affects your page’s load performance and SEO, allowing for targeted optimizations.
For instance, by identifying and eliminating unnecessary JavaScript blocking the main thread, we improved our site’s Speed Index and Time to Interactive, which are crucial for a robust SEO standing and enhanced user experiences.
In our internal tests, refining the use of JavaScript with these tools has consistently led to improved organic search performance across our project portfolios.

In my role as the founder and president of Raincross, a premier agency specializing in digital marketing and web technologies, I’ve extensively tackled challenges and strategies involving JavaScript and on-page SEO.
One tactic that has proven successful in our projects is the use of Isomorphic Rendering (Universal Rendering). This approach ensures that while the user enjoys a rich interactive experience using JavaScript on the client side, search engines have access to a fully rendered HTML on the server side, which is crucial for content visibility and SEO.
During our implementations, we often faced the challenge of JavaScript blocking the visibility of important on-page content to search engines.
To address this, we prioritized critical JavaScript and utilized server-side rendering (SSR) to ensure search engines could crawl and index our site’s content effectively before any client-side JavaScript was loaded.
This approach not only enhanced our SEO performance but also maintained the interactive qualities of client-side JavaScript, crucial for user engagement.
For startups looking to optimize their use of JavaScript for SEO, I strongly recommend implementing Lazy Loading techniques.
By deferring the loading of JavaScript until necessary, you ensure that the initial load of your site is quick and that critical content is indexed by search engines up front.
Additionally, utilizing tools like Google’s Lighthouse has been instrumental for Raincross in analyzing how JavaScript affects performance, allowing us to make precise optumizations that bolster both SEO and user experience.
By focusing on these key strategies, you can maintain a strong balance between dynamic content interaction facilitated by JavaScript and foundational SEO practices.

In my capacity as the founder and owner of Ronkot Design, our team often faces the challenge of integrating JavaSvript into our web designs without compromising on-page SEO. One successful example was during a project where the client required highly interactive web features.
To prevent typical SEO pitfalls associated with heavy JavaScript, we implemented server-side rendering (SSR).
This allowed the content, which was crucial for SEO, to load independently of the client’s interactions that relied on JavaScript. This method significantly enhanced page indexing by search engines without sacrificing user experience.
Specifically, one challenge we tackled was the slow loading time caused by large JavaScript files, which can negatively affect both user experience and SEO rankings.
We addressed this by adopting code splitting, a technique where JavaScript is divided into smaller chunks and only the necessary pieces are loaded with specific user actions.
This not only improved load times but also reduced the initial payload, enhancing SEO. For startups looking to optimize their JavaScript usage for better SEO, it’s critical to focus on loading essential JavaScript first and defer the rest.
This can be achieved through techniques such as asynchronous loading and code splitting.
Additionally, employing tools like Google’s Chrome Lighthouse has been invaluable in our workflow. It helps us analyze and optimize the web pages by providing specific metrics on performance and suggesting actionable improvements.
A concrete example from our experience involved using Lighthouse to identify unnecessary JavaScript loading early in the user journey, which we then optimized to achieve better performance scores and improve our client’s site visibility in search results.

Using JavaScript in web development has changed the way on-page SEO strategies are implemented.
There are still issues even though search engine crawlers are getting better at comprehending content produced with JavaScript.
JavaScript-generated dynamic material might not be easily indexed, affecting a website’s search engine ranking.
Furthermore, using less JavaScript might cause pages to load more slowly, which is good for SEO rankings.
Developers use strategies like pre-rendering and server-side rendering to ensure that material is accessible to search engine bots to address these problems.
JavaScript code performance optimization also improves user experience and improves search engine optimization.
Keeping up with JavaScript’s evolving effects on SEO and applying best practices is essential to preserving your competitive advantage in online visibility.

In my role as CEO at PlumbDev, I’ve navigated the complexities of using JavaScript on websites without harming on-page SEO. JavaScript, when not handled correctly, can obscure content from search engines, affecting site visibility and indexing.
To address this, we’ve implemented dynamic rendering. Essentially, dynamic rendering serves a version of the page that’s fully rendered to search engines while maintaining a rich, interactive version for users.
This approach has proven effective in maintaining robust user interactions without sacrificing SEO. One significant challenge with JavaScript is its potential to delay page loading times, which negatively impacts SEO rankings.
To combat this, we adopted the practice of lazy loading for our JavaScript-heavy sites. This technique only loads scripts necessary for the current part of the page being viewed, significantly improving load times and, as a result, SEO performance.
We monitored this through core web vitals, observing noticeable improvements in loading times across client projects, directly correlating to better search engine rankings.
For startups looking to optimize JavaScript for better search engine visibility, my advice is to prioritize critical JS loading and defer anything non-essential.
Tools like Google’s Lighthouse can be instrumental in identifying what scripts impact load times and how they can be optimized.
Moreover, consider leveraging server-side rendering (SSR) when possible, as this renders JavaScript on the server, sending a fully composed page to the client, making it immediately crawlable by search engines.
In our experience at PlumbDev, SSR has not only boosted SEO but also enhanced overall site performance, making it a win-win for user experience and search visibility.

In my tenure as the founder of That Local Pack, specializing in local SEO strategies, I’ve tackled the unique quandaries presented by JavaScript with regard to on-page SEO optimizations.
A compelling approach we’ve applied successfully is the use of Hybrid Rendering. Prioritizing the server-side rendering for essential content ensures that search engines index our client’s site content reliably.
Meanwhile, client-side processes enhance user interactions without interfering with the SEO friendliness of the page.
One significant hurdle we’ve encountered is JavaScript’s tendency to influence the load time detrimentally. To navigate this, we implemented code splitting where JavaScript functionalities are broken down into smaller, more manageable chunks.
This strategy loads only the necessary scripts as needed by the user’s interaction with the page, dramatocally improving load times and overall SEO performance.
This method has been instrumental, particularly for our clients in the auto services and home repair industries, where page speed and immediate information are crucial for customer retention.
For startups aiming to fine-tune their JavaScript for better search engine results, I strongly suggest focusing on the parsing and execution times of your scripts.
Utilize Google Chrome’s DevTools to simulate and test your pages under varying conditions and pinpoint bottlenecks caused by JavaScript. Continuously iterating on feedback from these tools allows you to make data-driven decisions that enhance both user experience and SEO.
Our proactive adjustments based on such analytics have consistently afforded our clients with improved visibility and increased organic traffic.

As the CEO of a digital marketing and web design agency, I have overseen numerous projects where JavaScript’s integration was crucial without sacrificing on-page SEO. Here are my insights based on real-world implementations and solutions:
1. Successful JavaScript Implementation and SEO:
Progressive Enhancement: We ensure that the core content of the website is accessible even if JavaScript fails to load. This approach guarantees that search engines can crawl and index our site’s primary content, thereby preserving SEO integrity.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): For dynamic websites built with JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular, we implement server-side rendering.
This means the browser receives fully rendered HTML from the server, making the content accessible to search engines before any JavaScript is executed.
2. Challenges and Solutions:
Delayed Indexing: JavaScript can delay the indexing of content as search engines need more resources to fetch, compile, and execute JavaScript. We’ve countered this by using dynamic rendering, serving static HTML versions of the pages to bots while keeping the interactive experience for users.
SEO Metrics Monitoring: Regularly monitoring SEO performance with tools like Google Search Console helps us identify if a JavaScript feature impacts our SEO negatively, allowing us to adjust our strategies promptly.
3. Tips for Startups:
Minimize Inline JavaScript: Keep inline scripts to a minimum. External scripts can be deferred or made asynchronous so they do not block the rendering of the page.
Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images and non-critical scripts. This not only improves page load times but also ensures that critical content is indexed by search engines first.
Structured Data: Use structured data to help search engines understand page content. This is particularly important in JavaScript-heavy sites where semantic HTML might be minimal.
4. Effective Tools and Techniques:
Google Lighthouse and PageSpeed Insights: Use these tools to evaluate how JavaScript affects performance and accessibility, which are crucial factors for SEO.
Webpack Bundle Analyzer: Reducing JavaScript bundle size is critical for performance. This tool helps visualize the size of JavaScript files, identifying opportunities to split and defer loading large bundles.
SEO-Friendly SPA Techniques: For single-page applications, utilize the History API to update URLs and make use of server-side rendering or pre-rendering services to ensure content is crawlable.
5. Case Studies and Experiences:
E-commerce Platform Optimization: For an e-commerce client, we converted their heavy client-side rendered site to use React with server-side rendering.
This change resulted in a 50% increase in organically acquired traffic by improving the load time and crawlability.
Blog Platform Revamp: Another project involved transitioning a blog from a traditional CMS to a JavaScript-heavy site. By implementing dynamic rendering, we maintained the site’s SEO performance, while enhancing interactivity and visual appeal.
Through these experiences, we’ve learned that while JavaScript can make websites dynamic and engaging, it must be implemented thoughtfully to ensure SEO is not compromised.
For startups, the key is to balance functionality with SEO fundamentals, continuously monitoring and optimizing as part of your growth strategy.

With over a decade of expertise, I specialize in developing strategies that enhance business visibility and growth through effective JavaScript integration.
I am eager to share my insights and experiences to help startups optimize their JavaScript for better search engine visibility, grounded in proven outcomes.
One critical strategy for successfully integrating JavaScript without compromising on-page SEO is server-side rendering (SSR). We applied SSR in a real-world scenario with a client’s large e-commerce platform, which was struggling with search engine visibility due to heavy JavaScript use.
By implementing SSR, we ensured that the content, including product descriptions and reviews, was fully rendered on the server side before reaching the user’s browser. This change led to a 50% organic traffic boost within three months. This demonstrates that SSR can effectively make dynamic content SEO-friendly.
However, employing JavaScript isn’t without its challenges. Initially, we faced significant issues with delayed content indexing, which impacted the site’s SEO performance.
We overcame this by optimizing the script management process and prioritizing the loading of critical JavaScript while deferring less crucial scripts. This improved indexing and enhanced the overall user experience by speeding up page load times.
For startups looking to optimize JavaScript, I recommend focusing on script efficiency. Tools like Google’s Lighthouse are invaluable for diagnosing performance issues and guiding optimizations.
Moreover, implementing Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) can significantly benefit SEO. In one case, after transitioning a client’s site to a PWA, we noticed improved user engagement and session duration, both positive signals to search engines.
Effective JavaScript SEO involves strategic script management and innovative solutions like SSR and PWAs. These technologies address SEO concerns and elevate the user experience, driving better engagement and visibility.

Understanding how JavaScript affects rendering and indexing is of the utmost importance in the field of on-page search engine optimization (SEO).
There is a possibility that traditional web crawlers will have difficulty handling content that is heavy on JavaScript, which could result in inadequate indexing and decreased search visibility.
Through the utilization of server-side rendering (SSR) or pre-rendering techniques, search engines are guaranteed to receive information that has been fully rendered, hence improving crawlability and indexing accuracy.
Additionally, expediting page loading, which is an essential ranking element, can be accomplished by optimizing JavaScript code for performance.
On-page search engine optimization (SEO) results can be improved by striking a balance between dynamic and interactive content and accessibility to search engines.

JavaScript can be challenging for SEO as search engines may struggle to render and index content generated by JavaScript. To mitigate this, it’s crucial to ensure that the content critical for SEO (like headings, descriptions, main content) is loaded in the initial HTML response.
Techniques such as Server-Side Rendering (SSR) or Static Site Generation (SSG) are often used. For instance, frameworks like Next.js allow for SSR and SSG, making it easier to build SEO-friendly React applications.
Challenges faced when using JavaScript and how you overcame them.
One common challenge is the delay in content visibility to search engine crawlers due to client-side rendering.
Overcoming this involves pre-rendering content on the server so that the initial page load provides all necessary SEO-relevant data.
Another issue is the potential for increased page load times with heavy JavaScript applications.
To address this, optimizing script loading is crucial—using techniques like code splitting, lazy loading components, and minimizing third-party scripts can help.
Tips and tricks for startups to optimize JavaScript for better search engine visibility.
Use SSR for delivering a full page content snapshot to the search engine, then hydrate the page with client-side JavaScript for interactivity.
Also, build functionality for the lowest common denominator first (no JavaScript), then enhance progressively for environments with JavaScript.
Finally, use tools like Google’s Lighthouse to audit your JavaScript applications. Pay attention to metrics related to SEO and performance and adjust accordingly.
Any specific tools or techniques that have been particularly effective in your experience.
Google Search Console – Essential for understanding how your site is performing in search and how it’s being crawled and indexed.
JavaScript Rendering vs. Static HTML: A SEO Perspective
At the heart of the JavaScript-SEO discussion lies the comparison between JavaScript-rendered content and static HTML content. Both have their merits and demerits from an SEO standpoint, making this comparison a cornerstone of our discussion.
Static HTML stands as the old guard of web content. It’s straightforward, with content directly embedded in the page’s HTML, making it readily accessible to search engines. The simplicity of static HTML means that search engines can easily crawl and index the content, ensuring it’s quickly visible in search results.
JavaScript-rendered content, however, introduces an additional layer of complexity. When a user accesses a JavaScript-heavy page, the browser runs the JavaScript to generate content. This dynamic generation offers a rich, interactive user experience but comes at a cost. Search engines need to execute the JavaScript to “see” the content, akin to a browser, which can introduce delays in crawling and indexing.
The SEO Implications
The divergence in how search engines handle JavaScript and static HTML has significant SEO implications. Static HTML content is almost immediately available for indexing, offering a straightforward path to visibility in search results. JavaScript-rendered content, though, might face indexing delays as search engines need to render the JavaScript to access the content.
This delay doesn’t mean JavaScript is an SEO deal-breaker. Instead, it highlights the need for strategic JavaScript usage, ensuring search engines can efficiently process and index your content. Balancing JavaScript’s interactive capabilities with search engine friendliness becomes a pivotal strategy.
Embracing Best Practices
To bridge the gap between JavaScript’s dynamic capabilities and the need for SEO-friendly content, adopting best practices is key. Techniques such as server-side rendering (SSR) and dynamic rendering offer pathways to make JavaScript-heavy pages more palatable to search engines. These methods allow for a hybrid approach, where search engines can access a static HTML version of the content, while users enjoy the rich interactivity JavaScript offers.
Strategic JavaScript Use: Balancing Act for Visibility and Engagement
At the core of leveraging JavaScript effectively is understanding its impact on the visibility of your website to search engines and the engagement experience of your users. The challenge lies in using JavaScript to create dynamic, interactive user experiences without compromising the site’s ability to be indexed and ranked by search engines. This balancing act is crucial for startup founders who need to ensure that their innovative platforms reach their intended audience.
Crafting User-First Experiences with JavaScript
Start with the user in mind. JavaScript enables startups to create immersive, interactive web applications that can set them apart from the competition. However, it’s essential to prioritize the user experience by focusing on performance and accessibility. Ensure that your use of JavaScript enhances the site’s functionality without overloading it with unnecessary scripts that could slow down page loading times. Remember, a faster site not only pleases users but also ranks better in search engine results.
SEO-Friendly JavaScript Techniques
While embracing the capabilities of JavaScript, employ techniques that mitigate its potential downsides on SEO. Consider server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation (SSG) for critical content pages to ensure they’re fully indexable by search engines. These approaches allow the content to be rendered on the server or at build time, making it immediately available to search engine crawlers without the need for JavaScript execution.
Progressive Web Apps: A Startup’s Ally
For startups, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) present a compelling opportunity to harness the best of web and mobile app worlds. PWAs use modern web capabilities to deliver app-like experiences in a browser, relying heavily on JavaScript. They are fast, reliable, and engaging, which can significantly enhance user satisfaction and retention.
Leveraging PWAs for SEO and Engagement
To make the most of PWAs while maintaining SEO performance, ensure your PWA is indexable and linkable. Use web app manifests and service workers strategically to speed up load times and enable offline functionality, but keep your content accessible to search engine crawlers. A well-implemented PWA can boost engagement and keep your startup at the forefront of innovation.
Continuous Optimization and Monitoring
The digital landscape is ever-changing, and what works today may not be as effective tomorrow. Continuous optimization and monitoring are vital. Utilize tools like Google Search Console and Lighthouse to track how well your site performs in search rankings and identify areas for improvement. Regular audits can reveal insights into how JavaScript impacts your SEO and where optimizations can be made to enhance both visibility and user experience.
Startup founders must navigate the complexities of JavaScript with a strategic mindset, balancing the innovative capabilities it offers with the foundational needs of SEO. By focusing on creating user-first experiences, employing SEO-friendly JavaScript techniques, embracing the potential of PWAs, and committing to continuous optimization, startups can achieve the visibility and engagement necessary to thrive in the competitive digital ecosystem.
Enhancing SEO with JavaScript: The Strategic Playbook

Embracing JavaScript without compromising on SEO calls for a nuanced approach. The following strategies are designed to ensure your site remains both dynamic and discoverable.
Prioritize Content Visibility in JavaScript
One of the primary concerns with JavaScript is ensuring that the content critical for SEO is visible to search engines. Here’s how:
- Critical Content First: Ensure that your most important content, especially textual content like articles, product descriptions, and blog posts, is accessible without requiring JavaScript. This might mean structuring your HTML to include essential content directly or using techniques like dynamic rendering to serve a JavaScript-free version to search bots.
- Progressive Enhancement: Adopt a progressive enhancement strategy. Begin with a basic, functional HTML version of your page, then layer on JavaScript for additional interactivity. This ensures that the core content and functionality are accessible to both users and search engines, regardless of JavaScript.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) for SEO-Friendly JavaScript
Server-side rendering is a powerful technique to make JavaScript-heavy sites search-friendly. SSR involves generating the full HTML for a page on the server in response to a navigation request. This pre-rendered page is then sent to the client, ensuring that the content is immediately visible to both users and search engine crawlers.
- SEO Benefits of SSR: By sending a fully rendered page from the server, you eliminate the need for search engines to execute JavaScript to access content. This speeds up the indexing process and ensures that your content is quickly visible in search results.
- User Experience Perks: SSR also enhances the user experience, particularly on mobile devices or in areas with slow internet connections, as it allows for faster initial page loading times.
Dynamic Rendering as an SEO Bridge
Dynamic rendering serves as a bridge for sites where SSR is not feasible due to technical constraints or the interactive nature of the site. It involves detecting the user agent of the requester (whether it’s a bot or a human user) and serving a static HTML version to bots and the regular JavaScript-heavy version to users.
- Implementing Dynamic Rendering: Tools and services like Puppeteer or Rendertron can be used to implement dynamic rendering. These tools generate static HTML versions of your JavaScript-heavy pages, ensuring that search bots can crawl and index your content without needing to render JavaScript.
Leveraging Structured Data for Enhanced Visibility
Structured data is a crucial component of SEO that can significantly enhance your site’s visibility in search results, especially for JavaScript-heavy sites. It involves using schema.org vocabulary to mark up your content, making it easier for search engines to understand and index.
- Boosting JavaScript SEO with Structured Data: Even if your JavaScript-driven content is dynamically loaded, you can embed structured data within the HTML to ensure that critical information about your content is immediately accessible to search engines.
- Rich Snippets and Enhanced Search Presence: Properly implemented structured data can lead to rich snippets, which enhance your visibility in search results and can lead to higher click-through rates.
Monitoring and Optimizing with SEO Tools
Finally, continuously monitor and optimize your site’s SEO performance. Use tools like Google Search Console and Lighthouse to identify issues with JavaScript rendering, mobile usability, and other SEO factors.
- Google Search Console: Offers insights into how Google views your site, highlighting issues with mobile usability, indexing, and rendering that can impact your SEO.
- Lighthouse: An open-source tool that provides audits of performance, accessibility, progressive web apps, SEO, and more, helping you identify areas for improvement.
By integrating these strategies into your development process, you can ensure that your JavaScript-heavy site offers a dynamic user experience without sacrificing its SEO performance. The key lies in understanding the balance between interactivity and accessibility, ensuring that your site is as appealing to search engines as it is to your users.
Advanced Performance Optimization: Speed Matters

In the digital realm, speed is king. A swift-loading site not only enhances user experience but also significantly impacts SEO rankings. For JavaScript-heavy sites, optimizing performance requires a multifaceted approach:
Minimize JavaScript Load Time
- Code Splitting: Implement code splitting to divide your JavaScript into smaller chunks. This ensures that users only download the code necessary for the initial page load, significantly reducing load time.
- Lazy Loading: Use lazy loading for images, scripts, and even modules. By loading resources only when they’re needed (e.g., when scrolling down the page), you can improve initial page load times and reduce server load.
- Optimize and Minify JavaScript Files: Compress and minify JavaScript files to decrease their size. Tools like Terser or UglifyJS can automate this process, stripping out unnecessary characters and whitespace without affecting functionality.
Leverage Browser Caching
Browser caching allows frequently used resources (like JavaScript files) to be stored locally in the user’s browser. This reduces load times on subsequent visits, as the browser doesn’t need to re-download these resources. Set appropriate cache-control headers for your JavaScript files to make effective use of browser caching.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN can drastically improve the loading speed of your JavaScript-heavy site for users around the world. By hosting your JavaScript files on a network of servers globally, a CDN ensures that these files are delivered from the server closest to the user, reducing latency and improving site speed.
Mobile-First Development and SEO
With the majority of internet traffic now coming from mobile devices, adopting a mobile-first approach is crucial for both user experience and SEO. For JavaScript-heavy sites, this means:
- Responsive Design: Ensure your site’s design is responsive, automatically adjusting to fit the screen size and resolution of the device it’s being viewed on. This is particularly important for interactive elements and layouts created with JavaScript.
- Touch Optimization: Optimize for touch interactions. JavaScript interactions that work well with a mouse and keyboard may not translate smoothly to touchscreens. Test and refine touch-based interactions to ensure they’re intuitive and responsive.
- Performance on Mobile: Given the typically slower network speeds and less powerful processors on mobile devices, optimizing the performance of your JavaScript is even more critical. Prioritize mobile performance from the start of your development process.
The Essence of Mobile-First in the Startup World
Mobile-first design prioritizes the development of websites and applications for mobile devices before making adjustments for desktop or larger screens. This approach is crucial for startups because it aligns with the behaviors and preferences of the modern consumer, who increasingly relies on mobile devices for information, entertainment, and shopping.
Optimizing for Mobile Speed and Performance
The cornerstone of a successful mobile-first strategy is speed. Mobile users expect quick, responsive interactions, and even a few seconds of delay can lead to frustration and abandonment. Startups must optimize their digital assets for speed, leveraging techniques such as compressing images, minifying CSS and JavaScript files, and utilizing AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) to ensure lightning-fast page loads. These efforts not only enhance user experience but also contribute positively to SEO, as search engines prioritize fast-loading sites in their rankings.
Navigating the Mobile SEO Landscape
Understanding the nuances of mobile SEO is essential for startups looking to gain visibility in a crowded marketplace. Mobile SEO goes beyond traditional desktop strategies, encompassing factors like local search optimization, voice search readiness, and mobile-friendly navigation. Ensuring that your site is responsive and adheres to Google’s mobile usability standards is just the beginning. Startups must also consider how users interact with their mobile devices, optimizing for touch-based navigation and designing for thumb-friendly interfaces.
Building for the Future: PWA as a Strategic Asset
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) represent a forward-thinking approach to mobile-first development, combining the best features of mobile sites and native applications. For startups, adopting PWA technology can be a game-changer, offering users a seamless, app-like experience without the need for downloading an app from a store. PWAs are inherently mobile-first, designed to work flawlessly on any device while taking advantage of features like offline operation, push notifications, and background syncing.
Leveraging PWA for Enhanced Engagement and Conversion
Integrating PWA technology into your mobile-first strategy can significantly boost engagement and conversion rates. By providing a fast, reliable, and engaging user experience, PWAs help startups retain users and encourage repeat visits. Moreover, the app-like nature of PWAs can enhance brand presence on users’ devices, keeping your startup top-of-mind and easily accessible.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The mobile landscape is continuously evolving, with new technologies, user preferences, and search engine algorithms emerging regularly. For startups, staying informed and adaptable is key to maintaining a competitive edge in the mobile-first arena. Regularly auditing your mobile site for SEO and usability, keeping abreast of the latest mobile development trends, and being willing to pivot your strategy in response to new insights are all crucial for sustained success.
In sum, for startups in today’s digital age, embracing a mobile-first development strategy is not optional—it’s essential. By prioritizing mobile speed and performance, understanding mobile SEO intricacies, exploring the potential of PWAs, and committing to continuous learning and adaptation, startups can set themselves up for growth, engagement, and success in the mobile-dominated online world.
The Role of A/B Testing in SEO and User Experience
A/B testing, or split testing, involves comparing two versions of a web page to see which performs better in terms of user engagement and conversion rates. For sites relying heavily on JavaScript, A/B testing can also reveal insights into how different JavaScript implementations affect SEO and user experience.
- Test Loading Strategies: Experiment with different JavaScript loading strategies (such as asynchronous vs. defer attributes) to find the optimal balance between functionality and performance.
- Evaluate Interactive Elements: Use A/B testing to refine the user interaction with JavaScript-driven elements. Minor changes in animation speed, interaction design, or even button placement can have significant effects on user engagement and conversion rates.
Integrating A/B Testing into Growth Strategies
A/B testing should be more than an occasional experiment; it needs to be woven into the fabric of a startup’s growth strategy. This involves a continuous cycle of hypothesizing, testing, learning, and iterating across all facets of the digital experience, from landing pages to blog posts, and call-to-action buttons to navigation layouts. By adopting a culture of testing and data-driven decision-making, startups can enhance their understanding of customer behavior and preferences, leading to more effective SEO and UX strategies.
Crafting Hypotheses with SEO and UX in Mind
The foundation of any successful A/B test is a strong, clear hypothesis that aligns with business goals and user needs. Startups should focus on creating hypotheses that target specific SEO and UX objectives, such as improving page load times, increasing click-through rates from search engine results pages (SERPs), or enhancing the usability of key website features. This strategic focus ensures that every test provides actionable insights, whether confirming a theory or offering unexpected lessons.
Bridging SEO and UX Through A/B Testing
While SEO aims to attract visitors and UX seeks to keep them engaged, A/B testing serves as the bridge between these two disciplines. For instance, testing different headline variations can reveal what language resonates most with your audience, influencing both SERP click-through rates (a key SEO metric) and user engagement levels (a core UX measure). Similarly, experimenting with the placement and wording of call-to-action buttons can impact both the site’s conversion rate (UX) and bounce rate (SEO), demonstrating how intertwined these aspects are.
Realizing the Full Potential of A/B Testing
To unlock the full potential of A/B testing, startups must adopt a holistic view, recognizing that small changes can have significant impacts. For example, testing the impact of adding schema markup to improve SERP appearance and click-through rates can provide SEO benefits, while also enhancing the user’s understanding of what to expect from the page, thus improving UX. Additionally, testing different forms of content presentation, such as video versus text for complex explanations, can offer insights into user preferences, aiding both SEO (by increasing on-page time) and UX (by improving content satisfaction).
Nurturing a Culture of Continuous Optimization
Embedding A/B testing into the startup ethos means nurturing a culture of continuous optimization. Encourage teams to regularly question assumptions, challenge the status quo, and seek improvement opportunities. Equipping teams with the right tools and resources to conduct and analyze A/B tests efficiently is crucial, as is fostering an environment where learning from ‘failures’ is valued as highly as celebrating successes.
In the dynamic startup ecosystem, where resources are precious and the margin for error is slim, A/B testing emerges not just as a tactic, but as a strategic imperative. By meticulously testing and optimizing SEO and UX elements, startups can ensure their digital platforms are primed for growth, engagement, and long-term success. This relentless pursuit of improvement, guided by the insights gained from A/B testing, can be the difference between stagnation and scaling.
Continual Learning and Adaptation
The digital landscape is perpetually evolving, with search engines regularly updating their algorithms. Staying informed about these changes and adapting your strategies accordingly is crucial for maintaining and improving your site’s SEO performance. Follow SEO news, participate in web development and SEO communities, and never stop testing and refining your approach.
By integrating these advanced practices into your SEO and development efforts, you can ensure that your JavaScript-heavy site not only delights users but also ranks well in search engine results. Remember, the ultimate goal is to create a seamless, engaging user experience that search engines can easily understand and rank.

Related: Check out our free SEO suite

Implementing Code Splitting in Your JavaScript Application
Code splitting is a technique that can significantly impact the performance of your JavaScript application, especially for on-page SEO. It involves breaking your app’s code into smaller chunks, which can then be loaded on demand. Here’s how to implement it effectively:
- Use Webpack for Bundling: Webpack is a popular static module bundler for JavaScript applications that supports code splitting out of the box. You can configure Webpack to create separate bundles for different parts of your application, which are then loaded only when needed.
- Dynamic Imports: JavaScript’s dynamic
import()syntax allows you to import modules on the fly. You can use this feature to split your code at logical breakpoints, such as loading a module only when a user performs a specific action.
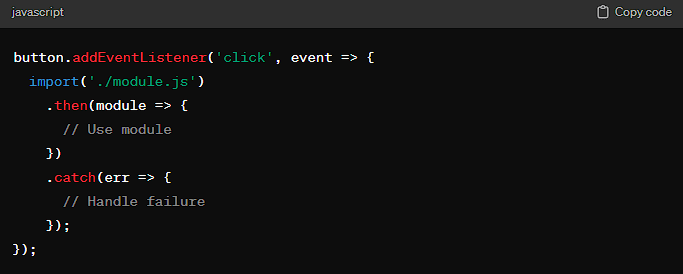
This approach ensures that users initially download only the core content of your application, reducing load times and improving SEO.
Optimizing Images with Lazy Loading
Images often account for the majority of a webpage’s size, impacting load times. Lazy loading delays the loading of images until they’re about to enter the viewport. Here’s a practical approach:
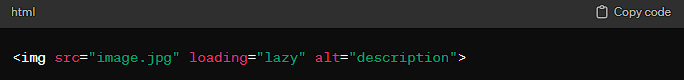
- HTML Native Lazy Loading: The simplest way to implement lazy loading is by using the
loading="lazy"attribute on your<img>and<iframe>tags. This native lazy loading is supported in most modern browsers and requires no additional JavaScript:
- JavaScript Libraries for Cross-Browser Support: For better control or support in older browsers, consider using a JavaScript library like Lozad.js or LazySizes. These libraries offer more flexibility and features, such as setting thresholds for when to start loading images.
Enhancing Mobile Performance with AMP
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is a web component framework designed to make pages load faster on mobile devices. While not a direct JavaScript optimization, using AMP can complement your JavaScript strategy for mobile:
- AMP as an SEO Strategy: Google prioritizes AMP pages in mobile search results, making it an effective strategy for boosting mobile SEO.
- Implement AMP alongside Your Main Site: Consider creating AMP versions of key pages, especially content-rich pages like articles and blog posts. This allows you to maintain a dynamic, JavaScript-heavy site for desktop and a fast, SEO-optimized version for mobile.
Conducting A/B Testing with Google Optimize
Google Optimize is a free tool that integrates with Google Analytics and allows you to run A/B tests on your site. It’s particularly useful for testing how changes to JavaScript-driven elements affect user behavior and SEO:
- Set Up Experiments for JavaScript Changes: Use Google Optimize to create experiments where you modify the JavaScript on a page. For example, test different loading strategies, interaction designs, or even content delivered via JavaScript.
- Analyze the Results: Monitor how the variations perform in terms of user engagement metrics and search rankings. Google Optimize provides detailed reports that can help you understand the impact of your changes.
By diving into these specific aspects and applying the outlined strategies, you can significantly improve the on-page SEO of your JavaScript-heavy site. Remember, the key to success lies in continuous testing, monitoring, and adapting to the ever-changing landscape of web development and search engine optimization.
Examples Of Implementing These Practices
Example: Code Splitting with React and Webpack
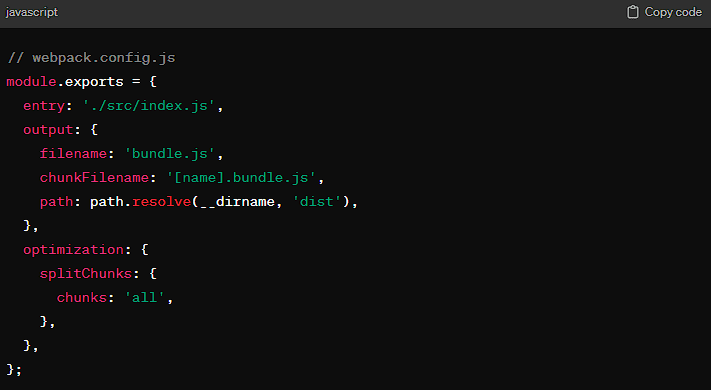
Let’s say you’re building a large React application. To improve its load time, you decide to implement code splitting for each major route.
Step 1: Configure Webpack for Code Splitting First, ensure your Webpack configuration supports code splitting. Webpack’s dynamic imports feature automatically takes care of splitting your code:
Step 2: Implement Dynamic Imports in React Use React.lazy for dynamic imports, combined with React Router for route-based code splitting:
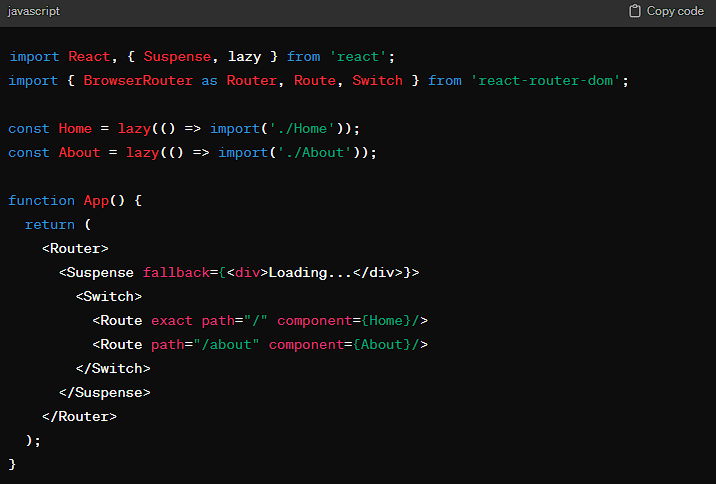
This setup ensures that the Home and About components are loaded only when the user navigates to their respective routes, significantly reducing the initial load time.
Example: Implementing Lazy Loading for Images in JavaScript
To implement lazy loading for images without relying on the native loading="lazy" attribute, you can use Intersection Observer API for better control and compatibility:
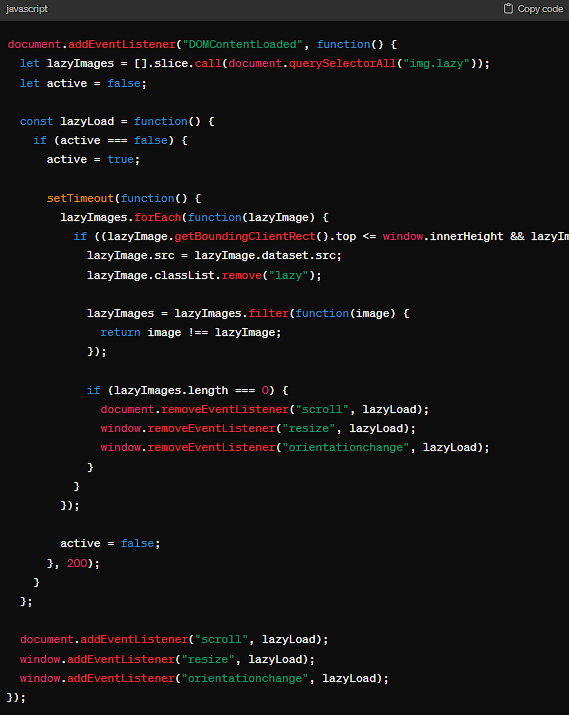
This code listens for scroll, resize, and orientation change events to check if any lazy-loaded images have entered the viewport. If so, it loads the image by setting the src attribute to the value of data-src.
Example: A/B Testing with Google Optimize
Imagine you want to test whether a faster-loading, less JavaScript-intensive version of your homepage leads to better engagement and lower bounce rates.
Step 1: Set Up the Experiment in Google Optimize
- Create a new experiment, selecting A/B test as your experiment type.
- Define two variants: the original homepage and a variant with optimized JavaScript (e.g., reduced libraries, implemented code splitting).
Step 2: Implement Variant with Optimized JavaScript For the variant, ensure that you have applied optimizations like code splitting and lazy loading. This might involve creating a separate entry point in your Webpack configuration for the variant or adjusting your code to use dynamic imports more aggressively.
Step 3: Analyze the Results
- Once the experiment is running, monitor the performance of each variant in Google Optimize.
- Look for differences in engagement metrics, such as time on page, bounce rate, and conversion rates.
By carefully implementing these practices and analyzing their impact through A/B testing, you can fine-tune your website’s performance and SEO strategy. These examples illustrate the tangible steps you can take to optimize your site, making it more engaging for users and more visible to search engines.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of JavaScript and on-page SEO, the key takeaway is the harmonious balance between leveraging JavaScript for dynamic user experiences and adhering to SEO best practices to ensure your content’s visibility. Through practical implementations of code splitting, lazy loading, and strategic A/B testing, we’ve uncovered the potential to significantly enhance site performance and search engine rankings.
Embracing these techniques not only improves user engagement but also solidifies your website’s presence in the competitive digital landscape. Remember, the evolution of web technologies and SEO standards is continuous, and staying informed and adaptable is crucial for success. By prioritizing both the technical and creative aspects of web development, you’re well on your way to creating websites that are not just functional and engaging but also SEO-friendly, ensuring they reach and resonate with your intended audience.
Read Next:
- How to Use Email Marketing Automation for Drip Campaigns
- The Complete Guide to International SEO: 2023 Best Practices!
- How to use Keap (formerly Infusionsoft): An Explainer
- How to use MailChimp: An Explainer
- 15 Best AI Marketing Tools to Elevate Your Business Growth






















Comments are closed.